Struts Interview Questions
Struts Interview Questions
Struts Interview Questions for Fresher
What is MVC ?
Model-View-Controller (MVC) is a design pattern put together to help control change. MVC decouples interface from business logic and data.
What is Model ?
The model contains the core of the application's functionality. The model encapsulates the state of the application.
Sometimes the only functionality it contains is state. It knows nothing about the view or controller.
What is view ?
The view provides the presentation of the model. The view can access the model getters, but it has no knowledge of the setters. In addition, it knows nothing about the controller. The view should be notified when changes to the model occur.
What is controller ?
The controller reacts to the user input. It creates and sets the model.
What is a framework ?
A framework is made up of the set of classes which allow us to use a library in a best possible way for a specific requirement.
What is Struts framework ?
Struts framework is an open-source framework for developing the web applications in JavaEE, based on MVC-2 architecture. It uses and extends the Java Servlet API.
Why use struts ?
Struts is robust architecture and can be used for the development of application of any size. Using struts you can easy design any size of application easily.
Explain Directory Structure of Struts Application ?
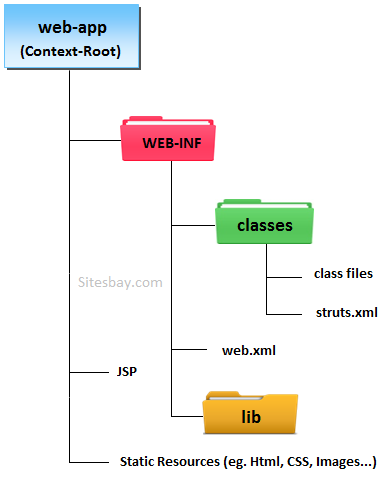
What are the components of Struts ?
Struts have mainly three components they are; Model, View and Controller:
Model: Components like business logic /business processes and data are the part of model.
View: Html and JSP are the view components.
Controller: Action Servlet of Struts is part of Controller components which works as front controller to handle all the requests.
What are the different kinds of actions in Struts ?
The different kinds of actions in Struts are:
- ForwardAction
- IncludeAction
- DispatchAction
- LookupDispatchAction
- SwitchAction
What are the core classes of the Struts Framework ?
Struts is a set of cooperating classes, servlets, and JSP tags that make up a reusable MVC 2 design.
What is ActionServlet ?
ActionServlet is a simple servlet which is the backbone of all Struts applications. It is the main Controller component that handles client requests and determines which Action will process each received request.
What is role of ActionServlet ?
ActionServlet performs the role of Controller:
- Process user requests
- Determine what the user is trying to achieve according to the request
- Pull data from the model (if necessary) to be given to the appropriate view,
- Select the proper view to respond to the user
- Delegates most of this grunt work to Action classes
- It is responsible for initialization and clean-up of resources
What is the ActionForm ?
ActionForm is javabean which represents the form inputs containing the request parameters from the View referencing the Action bean.
What are the important methods of ActionForm ?
The important methods of ActionForm are : validate() & reset().
Describe validate() and reset() methods ?
validate(): It is used to validate properties after they have been populated; Called before FormBean is handed to Action. Method signature for the validate() method is; public ActionErrors validate(ActionMapping mapping,HttpServletRequest request)
reset(): reset() method is called by Struts Framework with each request that uses the defined ActionForm. The purpose of this method is to reset all of the ActionForm's data members prior to the new request values being set. public void reset() {}.
What is ActionMapping?
Action mapping contains all the deployment information for a particular Action bean. This class is to determine where the results of the Action will be sent once its processing is complete.
What is DispatchAction ?
The DispatchAction class is used to group related actions into one class. Using DispatchAction class, you can have a method for each logical action compared than a single execute method.
What is the use of ForwardAction ?
The ForwardAction class is useful when you are trying to integrate Struts into an existing application that uses Servlets to perform business logic functions.
What is IncludeAction ?
The IncludeAction class is useful when you want to integrate Struts into an application that uses Servlets. Use the IncludeAction class to include another resource in the response to the request being processed.
What is the difference between ForwardAction and IncludeAction ?
Use IncludeAction only if the action is going to be included by another action or jsp. Use ForwardAction to forward a request to another resource in your application, such as a Servlet that already does business logic processing or even another JSP page.
What is LookupDispatchAction ?
The LookupDispatchAction is a subclass of DispatchAction. It does a reverse lookup on the resource bundle to get the key and then gets the method whose name is associated with the key into the Resource Bundle.
What is the use of LookupDispatchAction ?
LookupDispatchAction is useful if the method name in the Action is not driven by its name in the front end, but by the Locale independent key into the resource bundle.
Give various Struts tag libraries
Some Struts tag libraries are;
- HTML Tags
- Bean Tags
- Logic Tags
- Template Tags
- Nested Tags
- Tiles Tags
What is difference between LookupDispatchAction and DispatchAction ?
The difference between LookupDispatchAction and DispatchAction is that the actual method that gets called in LookupDispatchAction is based on a lookup of a key value instead of specifying the method name directly.
What is SwitchAction ?
The SwitchAction class provides a means to switch from a resource in one module to another resource in a different module. SwitchAction is useful only if you have multiple modules in your Struts application.
What if <action> element has <forward> declaration with same name as global forward ?
In this case the global forward is not used. Instead the <action> elementís <forward> takes precedence.
What is the use of <logic:iterate> ?
<logic:iterate> repeats the nested body content of this tag over a specified collection.
Syntax
<table border=1> <logic:iterate id="customer" name="customers"> <tr> <td><bean:write name="customer" property="firstName"/></td> <td><bean:write name="customer" property="lastName"/></td> <td><bean:write name="customer" property="address"/></td> </tr> </logic:iterate> </table>
How to display validation errors on jsp page ?
<html:errors/> tag displays all the errors. <html:errors/> iterates over ActionErrors request attribute.
What are the various Struts tag libraries ?
- HTML Tags
- Bean Tags
- Logic Tags
- Template Tags
- Nested Tags
- Tiles Tags
What are differences between <bean:message> and <bean:write> ?
<bean:message>: is used to retrive keyed values from resource bundle. It also supports the ability to include parameters that can be substituted for defined placeholders in the retrieved string.
Syntax
<bean:message key="prompt.customer.firstname"/>
<bean:write>: is used to retrieve and print the value of the bean property. <bean:write> has no body.
Syntax
<bean:write name="customer" property="firstName"/>
How the exceptions are handled in struts ?
Exceptions in Struts are handled in two ways;
Programmatic exception handling
Explicit try/catch blocks in any code that can throw exception. It works well when custom value (i.e., of variable) needed when error occurs.
Declarative exception handling
You can either define <global-exceptions> handling tags in your struts-config.xml or define the exception handling tags within <action></action> tag. It works well when custom page needed when error occurs. This approach applies only to exceptions thrown by Actions.
Syntax
<global-exceptions> <exception key="some.key" type="java.lang.NullPointerException" path="/WEB-INF/errors/null.jsp"/> </global-exceptions> or <exception key="some.key" type="package.SomeException" path="/WEB-INF/somepage.jsp"/>
What is the use of <logic:iterate> ?
<logic:iterate> repeats the nested body content of this tag over a specified collection.
Syntax
<table border=1> <logic:iterate id="customer" name="customers"> <tr> <td><bean:write name="customer" property="firstName"/></td> <td><bean:write name="customer" property="lastName"/></td> <td><bean:write name="customer" property="address"/></td> </tr> </logic:iterate> </table>
Describe reset() method ?
reset(): reset() method is called by Struts Framework with each request that uses the defined ActionForm. The purpose of this method is to reset all of the ActionForm's data members prior to the new request values being set.
Syntax
public void reset() {}
Describe validate() method ?
validate() : Used to validate properties after they have been populated; Called before FormBean is handed to Action. Returns a collection of ActionError as ActionErrors. Following is the method signature for the validate() method.
Syntax
public ActionErrors validate(ActionMapping mapping,HttpServletRequest request).
How is the Action Mapping specified ?
We can specify the action mapping in the configuration file called struts-config.xml. Struts framework creates ActionMappingobject from <ActionMapping> configuration element of struts-config.xml file.
Syntax
<action-mappings> <action path="/submit" type="submit.SubmitAction" name="submitForm" input="/submit.jsp" scope="request" validate="true"> <forward name="success" path="/success.jsp"/> <forward name="failure" path="/error.jsp"/> </action> </action-mappings>
What is role of Action Class ?
An Action Class performs a role of an adapter between the contents of an incoming HTTP request and the corresponding business logic that should be executed to process this request.
In which method of Action class the business logic is executed ? ?
In the execute() method of Action class the business logic is executed.
What design patterns are used in Struts ?
Struts is based on model 2 MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture. Struts controller uses the command design pattern and the action classes use the adapter design pattern. The process() method of the RequestProcessor uses the template method design pattern.
Can we have more than one struts config.xml file for a single Struts application ?
Yes, we can have more than one struts-config.xml for a single Struts application. They can be configured as follows;
Syntax
<servlet> <servlet-name>action</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.apache.struts.action.ActionServlet </servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>config</param-name> <param-value> /WEB-INF/struts-config.xml, /WEB-INF/struts-admin.xml, /WEB-INF/struts-config-forms.xml </param-value> </init-param> ..... <servlet>
What is the difference between session scope and request scope when saving formbean ?
when the scope is request,the values of formbean would be available for the current request. when the scope is session,the values of formbean would be available throughout the session.
What is DispatchAction ?
The DispatchAction class is used to group related actions into one class. Using this class, you can have a method for each logical action compared than a single execute method. The DispatchAction dispatches to one of the logical actions represented by the methods. It picks a method to invoke based on an incoming request parameter. The value of the incoming parameter is the name of the method that the DispatchAction will invoke.
What is the use of ForwardAction ?
The ForwardAction class is useful when youíre trying to integrate Struts into an existing application that uses Servlets to perform business logic functions. You can use this class to take advantage of the Struts controller and its functionality, without having to rewrite the existing Servlets. Use ForwardAction to forward a request to another resource in your application, such as a Servlet that already does business logic processing or even another JSP page. By using this predefined action, you donít have to write your own Action class. You just have to set up the struts-config file properly to use ForwardAction.
What is IncludeAction ?
The IncludeAction class is useful when you want to integrate Struts into an application that uses Servlets. Use the IncludeAction class to include another resource in the response to the request being processed.
What is the difference between ForwardAction and IncludeAction ?
The difference is that you need to use the IncludeAction only if the action is going to be included by another action or jsp. UseForwardAction to forward a request to another resource in your application, such as a Servlet that already does business logic processing or even another JSP page.
What is LookupDispatchAction ?
The LookupDispatchAction is a subclass of DispatchAction. It does a reverse lookup on the resource bundle to get the key and then gets the method whose name is associated with the key into the Resource Bundle.
What is the use of LookupDispatchAction ?
LookupDispatchAction is useful if the method name in the Action is not driven by its name in the front end, but by the Locale independent key into the resource bundle. Since the key is always the same, the LookupDispatchAction shields your application from the side effects of I18N.
What is SwitchAction ?
The SwitchAction class provides a means to switch from a resource in one module to another resource in a different module. SwitchAction is useful only if you have multiple modules in your Struts application. The SwitchAction class can be used as is, without extending.
What is DynaActionForm ?
A specialized subclass of ActionForm that allows the creation of form beans with dynamic sets of properties (configured in configuration file), without requiring the developer to create a Java class for each type of form bean.
How to display validation errors on jsp page ?
<html:errors/> tag displays all the errors. <html:errors/> iterates over ActionErrors request attribute.
What are the various Struts tag libraries ?
- HTML Tags
- Bean Tags
- Logic Tags
- Template Tags
- Nested Tags
- Tiles Tags
What are differences between <bean:message> and <bean:write> ?
<bean:message>: is used to retrive keyed values from resource bundle. It also supports the ability to include parameters that can be substituted for defined placeholders in the retrieved string.
Syntax
<bean:message key="prompt.customer.firstname"/>
<bean:write>: is used to retrieve and print the value of the bean property. <bean:write> has no body.
Syntax
<bean:write name="customer" property="firstName"/>
How the exceptions are handled in struts ?
Exceptions in Struts are handled in two ways;
Programmatic exception handling
Explicit try/catch blocks in any code that can throw exception. It works well when custom value (i.e., of variable) needed when error occurs.
Declarative exception handling
You can either define <global-exceptions> handling tags in your struts-config.xml or define the exception handling tags within <action></action> tag. It works well when custom page needed when error occurs. This approach applies only to exceptions thrown by Actions.
Syntax
<global-exceptions> <exception key="some.key" type="java.lang.NullPointerException" path="/WEB-INF/errors/null.jsp"/> </global-exceptions> or <exception key="some.key" type="package.SomeException" path="/WEB-INF/somepage.jsp"/>
What is the use of <logic:iterate> ?
<logic:iterate> repeats the nested body content of this tag over a specified collection.
Syntax
<table border=1> <logic:iterate id="customer" name="customers"> <tr> <td><bean:write name="customer" property="firstName"/></td> <td><bean:write name="customer" property="lastName"/></td> <td><bean:write name="customer" property="address"/></td> </tr> </logic:iterate> </table>

