Array in C
Array in C Language
An Array is a collection of similar data type value in a single variable. It is a derived data type in C, which is constructed from fundamental data type of C language.
Key Features of Array in C
marks[0] marks[1] marks[2] marks[3] marks[4]
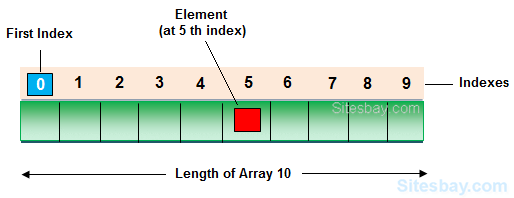
- Arrays have 0 (Zero) as the first index, not 1 (One). In this example, marks[0] is the first element.
- If the size of an array is N, to access the last element, the N-1 index is used. In this example, mark[4].
- Suppose the starting address of mark[0] is 2120d. Then, the address of the mark[1] will be 2124d. Similarly, the address of marks[2] will be 2128d and so on.
- This is because the size of a float is 4 bytes.
Why Do We Need Arrays ?
We can use normal variables like (var1, var2, var3, var4,.....) when we have a small number of objects, but if we want to store a large number of instances, then it becomes difficult to manage them with normal variables. To overcome this this problem we use concept of Array in Programming Language to represent many instances in one variable.
Advantage of array
- Code Optimization: Less code is required, one variable can store numbers of value.
- Easy to traverse data: By using array easily retrieve the data of array.
- Easy to sort data: Easily short the data using swapping technique
- Random Access: With the help of array index you can randomly access any elements from array.
Dis-Advantage of array
Fixed Size: Whatever size, we define at the time of declaration of array, we can not change their size, if you need more memory in that time you can not increase memory size, and if you need less memory in that case also wastage of memory.
Array Declaration in C
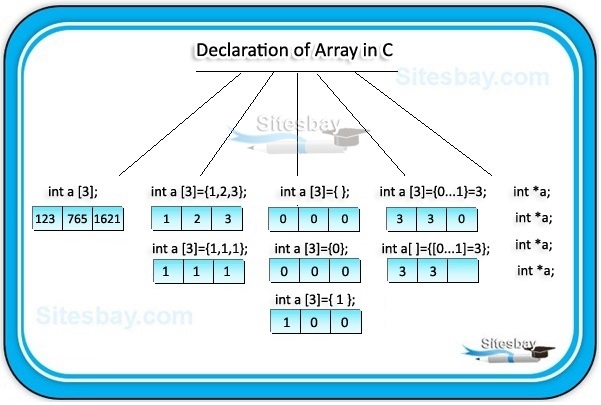
To declare an array in C you need to declare datatype and size of an Array or by initializing it or by both.
Array declaration by specifying size
Syntax
datatype arrayName[SIZE];
Syntax
// Array declaration by specifying size int arr1[10]; // declare an array of user specified size int n = 10; int arr2[n];
Array Declaration by Initializing Elements
Syntax
// Array declaration by initializing elements
int arr[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 }
// Here Compiler creates an array of size 4.
// above is same as "int arr[4] = {10, 20, 30, 40}"
Array declaration by specifying size and initializing elements
Syntax
// Array declaration by specifying size and initializing
int arr[6] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 }
In above syntax Compiler creates an array of size 6, initializes first 4 elements as specified by user and rest two elements as 0. above is same as "int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 0, 0}"
Example
int roll_no[10];
Initializing Array
Initializing is a process to initialize the value in array variable. This is happen in two ways, initialize array one by one or all elements are initializing once.
Initialization of array one by one
int arr[5]; arr[0]=10; arr[1]=20; arr[2]=30; arr[3]=40; arr[4]=50;
Initialization of array at once
int arr[]={10,20,30,40,50};
Accessing Array Elements in C
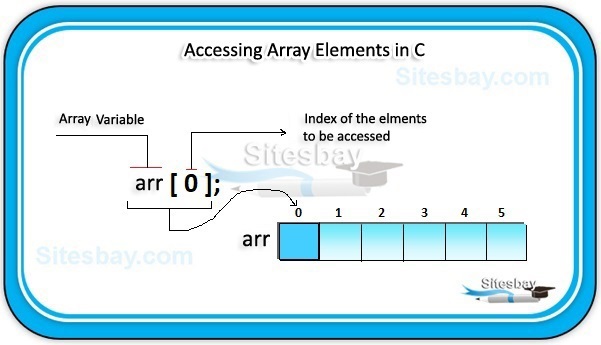
We can access array elements with the help of index value of element. Array index starts with 0 and goes till size of array minus 1.
Accessing Array Elements Example
int arr[]={10,20,30,40,50};
arr[3] // here 3 is index value and it return 40
Example of array
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int i, marks[]={80, 62, 70, 90, 98}; //declaration and initialization of array
clrscr();
//traversal of array
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("\n%d",marks[i]);
}
getch();
}
Example
80 62 70 90 98
2-dimentional array
- In 2-dimentional elements are arranged in row and column format.
- When we are working with 2-dimentional array we require to refer 2-subscript operator which indicates row and column sizes.
- The main memory of 2-dimentional array is rows and sub-memory is columns.
- On 2-dimentional array when we are referring one-subscript operator then if gives row address, 2-subscript operator will gives element.
- On 2-dimentional array arrayName always gives main memory that is 1st row base address, arrayName will gives next row base address.
Syntax
datatype arrayName[SIZE][SIZE];
Important points related to array
Always size of the array must be an unsigned integer value which is greater than '0' only. In declaration of the array size must be required to mention, if size is not mention then compiler will give an error.
Example
int arr[]; //error
In declaration of the array size must be assigned type which value is greater than 0. In initialization of the array if specific number of values are not initialized it then rest of all elements will be initialized with it '0'.
Example
int arr[5]={10,20}; // yes valid
arr[0]=10;
arr[1]=20;
arr[2], arr[3], arr[4]; // initialized with zero
In initialization of the array mentioning the size is optional, in this case how many elements are initialize it that many variable are created.
Example
int arr[]={10,20,30,40,50}; // valid
Size=5;
Sizeof(arr)=10 byte
Important points for Array
- In implementation when we required 'n' number of variables of same data type then go for an array.
- When we are working with arrays always memory will created in continues memory location, so randomly we can access the data.
- In arrays all elements will share same name with unique identification value called index.
- Always array index will start with '0' and end with 'size-1'.
- When we are working with array compile time memory management will occur that is static memory allocation.
Access Array Elements out of its bound!
Suppose you declared an array of 10 elements. Let's say,
Example
int Marks[10];
You can access the array elements from Marks[0] to Marks[9]. Now let's say if you try to access Marks[12]. The element is not available. This may cause unexpected output (undefined behavior). Sometimes you might get an error and some other time your program may run correctly.Hence, you should never access elements of an array outside of its bound.

